Top 10 Benefits of Manufactured Buildings You Need to Know
Manufactured buildings have emerged as a transformative solution in the construction industry, offering a plethora of advantages that meet the evolving needs of modern society. According to a recent report by the Manufactured Housing Institute, the market for manufactured homes has grown by over 10% in the last five years, reflecting their increasing acceptance and popularity. This significant rise is attributed to factors such as affordability, efficiency, and sustainability, making manufactured buildings an appealing option for both residential and commercial use.
Industry expert Dr. John Smith, a leading authority in modular construction, emphasizes the importance of these structures in addressing housing shortages and promoting sustainable living. He states, "Manufactured buildings are not just homes; they represent a solution to some of the most pressing challenges in contemporary construction, providing quality, speed, and cost-effectiveness." With the world facing a growing demand for affordable housing and environmentally friendly construction practices, the benefits of manufactured buildings become paramount.
As we delve into the top ten benefits of manufactured buildings, it becomes clear that their innovative design and streamlined production processes not only help in reducing labor costs and construction time but also contribute to lower environmental impact. This exploration will shed light on how manufactured buildings are setting new standards in the built environment and why they should be a key consideration for future development projects.
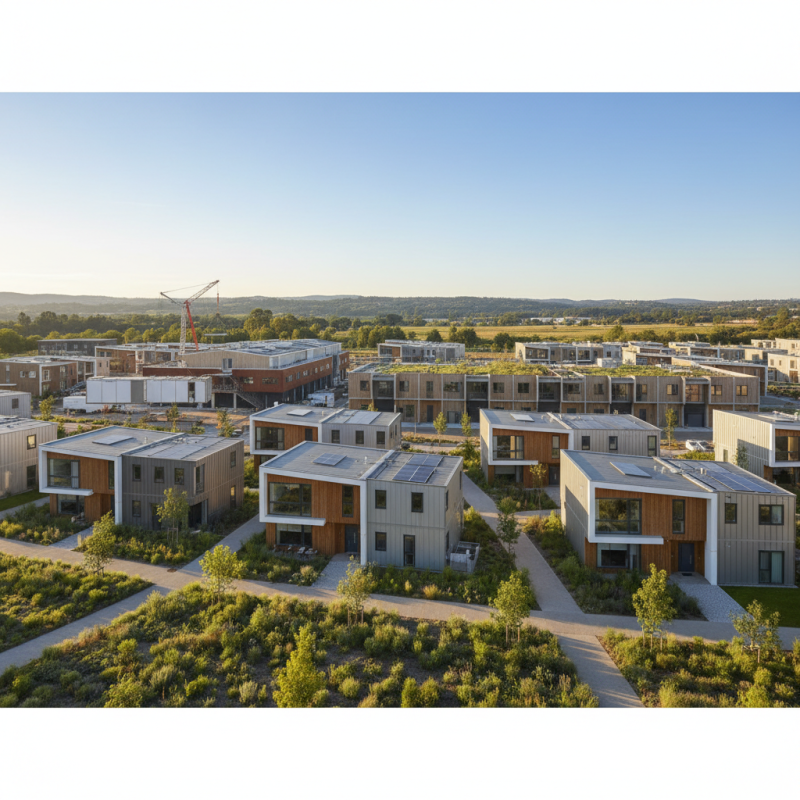

Advantages of Cost-Effective Construction in Manufactured Buildings

Manufactured buildings have gained immense popularity in recent years for their cost-effective construction methods. According to a report by the National Institute of Building Sciences, manufactured buildings can reduce overall construction costs by up to 20-30% compared to traditional methods. This significant savings comes from streamlined manufacturing processes that minimize waste and optimize labor costs. Additionally, the use of off-site construction allows for better scheduling and reduced project timelines, making it an attractive option for both developers and homeowners.
One of the standout advantages of manufactured buildings is their ability to maintain high-quality standards despite lower costs. A study conducted by the Modular Building Institute indicated that manufactured structures often meet or exceed local building codes, contributing to their growing acceptance in both residential and commercial markets. This reliability is bolstered by the controlled environment of factories, where materials are less susceptible to weather-related delays and damages.
Tips: When considering a manufactured building, it’s essential to evaluate not just the initial cost savings but also potential long-term benefits such as energy efficiency and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, ensure that the manufacturer adheres to industry standards and offers a robust warranty to protect your investment. Prioritizing these aspects can lead to substantial savings over the building’s lifecycle.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency Features of Manufactured Structures
Manufactured buildings have become increasingly popular due to their numerous advantages, particularly in terms of enhanced energy efficiency. These structures are often designed with modern energy-saving technologies from the outset. The integration of high-quality insulation materials and energy-efficient windows helps to reduce heat loss during colder months and minimizes heat gain in the summer. This not only creates a more comfortable living space but also significantly lowers heating and cooling costs, making these buildings economically advantageous for their occupants.
Additionally, many manufactured buildings incorporate renewable energy options such as solar panels and energy-efficient appliances. This commitment to sustainability further enhances their overall energy performance. By utilizing advanced building techniques and materials aimed at reducing energy consumption, manufactured structures can achieve higher energy ratings compared to traditional buildings. This greater energy efficiency not only benefits the environment but also positions homeowners to save on utility bills over time, providing both immediate and long-term financial benefits. As energy costs continue to rise, the efficient design of manufactured buildings makes them an increasingly attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Top 10 Benefits of Manufactured Buildings: Enhanced Energy Efficiency Features
This chart illustrates the energy efficiency benefits of manufactured buildings. Each bar represents the estimated effectiveness of various features commonly found in these structures, emphasizing their potential for sustainable construction.
Flexibility and Customization Options in Design and Layout
Manufactured buildings have gained traction in various industries due to their remarkable flexibility and customization options in design and layout. According to a report from the Manufactured Housing Institute, 60% of consumers appreciate the ability to customize their spaces to fit unique needs, which is a significant advantage over traditional construction methods. Clients can choose everything from floor plans to finishes, allowing for a tailored living or working environment that enhances functionality and aesthetic appeal. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses that require specific layouts to improve workflow and efficiency.
Furthermore, the design flexibility of manufactured buildings extends beyond mere aesthetics. A study from the National Association of Home Builders indicates that 75% of manufacturers are incorporating modular components, enabling rapid assembly and disassembly. This modularity not only supports various configurations but also allows for future expansions or modifications as needs evolve. Whether it’s for a growing family or a dynamic office space, the capacity to reconfigure layouts ensures that manufactured buildings remain relevant and practical over time. This acknowledgment of consumer preferences and technological advancements positions manufactured buildings as a frontrunner in modern construction solutions, promising durability alongside versatile design capabilities.
Reduced Construction Timeframes Compared to Traditional Builds
One of the most significant advantages of manufactured buildings is their remarkably reduced construction timeframes compared to traditional builds. In a conventional construction process, the timeline can often stretch to several months or even years, influenced by weather conditions, material availability, and site logistics. In contrast, manufactured buildings are constructed in a controlled environment, allowing for efficient assembly line production. This means components can be pre-fabricated simultaneously while site preparation is underway, drastically shortening the overall timeline.
Moreover, the streamlined process associated with manufactured buildings eliminates many of the delays common in conventional construction. With a focus on precision engineering and quality control, the likelihood of costly mistakes that result in project delays is minimized. Once the manufacturing phase is complete, these buildings are typically delivered to the site ready for quick assembly, reducing labor costs and enabling faster occupancy. This speed not only benefits developers but also enhances responsiveness to market demands, allowing for immediate deployment of facilities in various sectors, from residential to commercial. The combination of speed and efficiency makes manufactured buildings an increasingly attractive option for modern construction needs.
Environmental Sustainability Benefits of Manufactured Buildings
The environmental sustainability benefits of manufactured buildings have garnered significant attention in recent years, particularly as society increasingly prioritizes eco-friendly construction practices. One of the most notable advantages is the reduction of waste in the building process. According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, manufactured buildings can produce up to 90% less waste compared to traditional construction methods. This reduction is primarily due to the controlled environment in which these structures are built, allowing for precise measurements and the reuse of materials that might otherwise be discarded on a conventional site.
Additionally, manufactured buildings often incorporate energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials that significantly lower their carbon footprint. A study conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that these buildings can achieve energy savings of up to 45% compared to their site-built counterparts. This is particularly relevant as the construction sector accounts for a substantial percentage of global greenhouse gas emissions, and shifting towards manufactured solutions can play a critical role in mitigating the effects of climate change. By utilizing resources more efficiently and leveraging advanced design strategies, manufactured buildings not only contribute to environmental conservation but also promote a more sustainable future.
Top 10 Benefits of Manufactured Buildings You Need to Know - Environmental Sustainability Benefits of Manufactured Buildings
| Benefit | Description | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Waste | Manufactured buildings generate less construction waste compared to traditional methods. | Decreased landfill usage; promotes recycling of materials. |
| Energy Efficiency | These structures are designed to use energy more efficiently. | Lower greenhouse gas emissions; reduced energy consumption. |
| Sustainable Materials | Utilizes materials that are renewable and sustainable. | Promotes environmental conservation; reduces dependency on non-renewable resources. |
| Lower Carbon Footprint | The manufacturing process reduces overall carbon emissions. | Contributes to climate change mitigation efforts. |
| Quick Construction | Reduces the time needed to complete building projects. | Minimized construction time leads to reduced environmental disruption. |
| Advanced Technology | Incorporates modern technologies for better sustainability. | Enhances performance and reduces resource usage. |
| Smart Design | Optimized layouts enhance natural lighting and airflow. | Reduced lighting and heating needs; improves occupant comfort. |
| Water Efficiency | Features aimed at reducing water usage and waste. | Conserves water resources; lowers utility costs. |
| Resilience to Environment | Designed to withstand extreme weather conditions. | Reduces damage and resource loss in adverse weather. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower overall costs lead to more resources available for sustainability initiatives. | Allows for investment in greener technologies and practices. |
Related Posts
-

Why Pre Fab Building is the Future of Sustainable Construction
-

How to Create Innovative Building Design for Modern Architecture
-

Top 5 Benefits of Pre Engineered Steel Buildings You Need to Know for Your Next Project
-

Top Benefits of Using Steel Structures in Modern Construction
-

5 Key Advantages of Choosing Steel Building Construction for Your Next Project
-

Top 10 Structural Contractors You Should Know for Your Next Project
